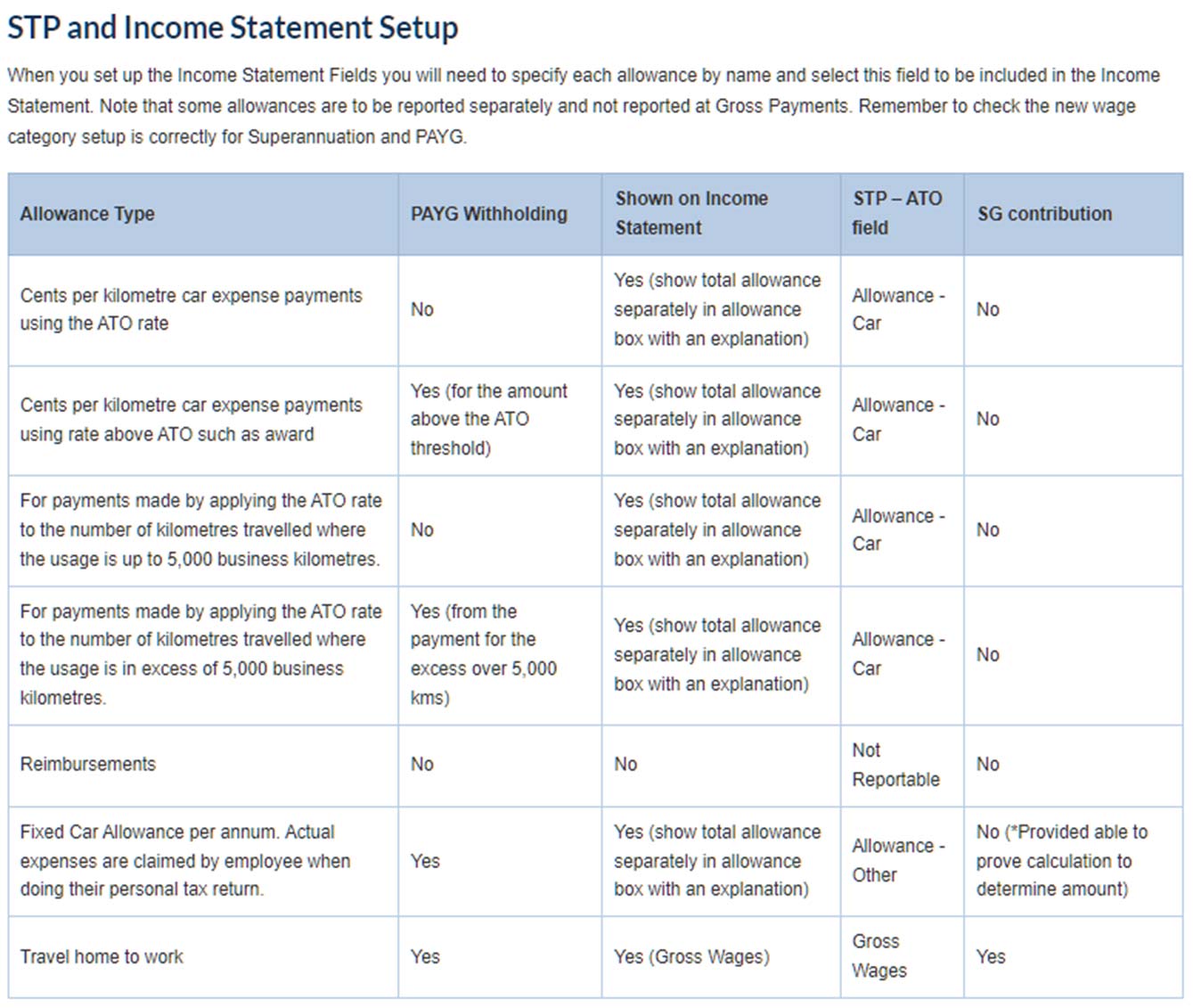
Allowances and STP 2
Allowances Explained
ICB have updated our resource ICB’s updated reference ICB – What is An Allowance. This resource now includes information on STP 1 and STP 2.
Allowances are usually a specifically identified amount paid in addition to an agreed salary. It is separately identified, and relates to such things as:
- Working conditions, e.g., danger and height allowances.
- Qualifications or special duties, e.g., first aid officer, leading hand.
- Expenses not claimable as a tax deduction, e.g., travel from home to work.
- Work-related expenses that can be claimed as a tax deduction, e.g., travel between work sites.
STP2 imposes additional reporting requirements for Allowances.

Don’t report: Reimbursements – These are an amount that reimburses an expense which was (or will be) incurred by the employee in the course of their duties and can be verified by receipts.
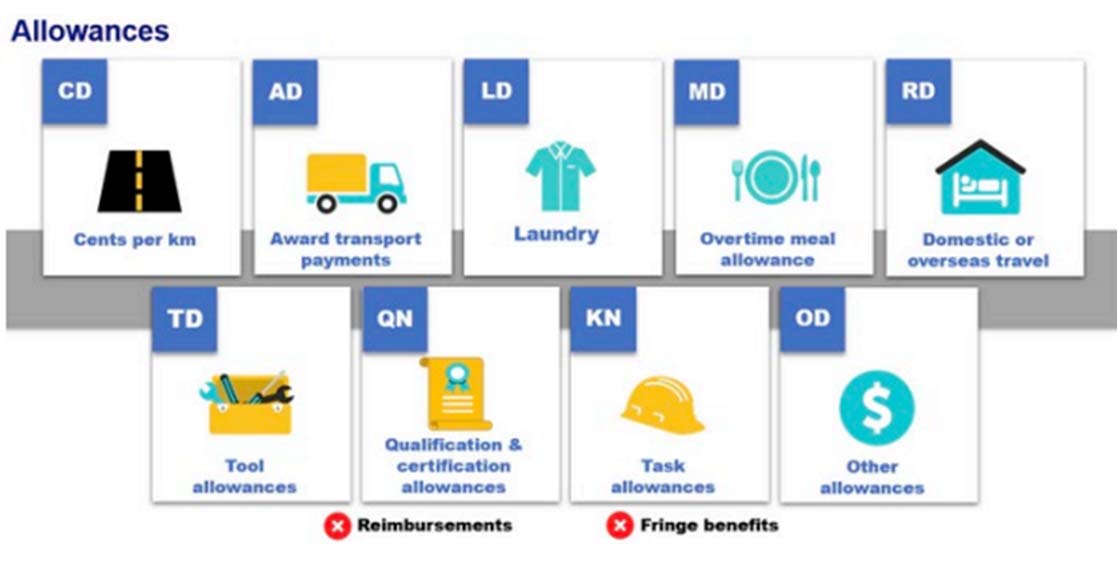
Types of Allowances
- Cents per km (allowance type CD).
- Award transport payments (allowance type AD).
- Laundry (allowance type LD).
- Overtime meal allowance (allowance type MD).
- Domestic or overseas travel (allowance type RD).
- Tool allowances (allowance type TD).
- Qualification and certification allowances (allowance type QN).
- Task allowances (allowance type KN).
Other Allowances
- GI (general). Laundry allowances for the cost of laundering deductible conventional clothing.
HI (home office). Home office equipment allowances. Internet allowances. - ND (non-deductible). Cents per km payments for private travel such as travel between home and
work. Allowance payments for the cost of transport for private purposes. Laundry allowance for
the cost of laundering uniforms for private purposes. Part-day travel allowances. Allowances paid
in relation to equipment used for private purposes. - TI (transport/fares). Allowance payments for the cost of transport for business related travel not
traceable to a historical award in force on 29th October 1986. - UI (uniform). Allowances paid for the purchase of a uniform.
- VI (private vehicle). Cents per km payments for vehicles otherthan a car such as a motorbike or van.
- Flat rate car allowance that is referable to the kilometres travelled.
Difference Between Allowances and Reimbursements
Allowances
Allowances are amounts paid to cover anticipated costs or as compensation for conditions of employment and are paid regardless of whether the employee incurs an expense. Allowances are assessable income to the employee and are generally included as income in their tax return. The employee may be entitled to claim a tax deduction. Typically, despite the level of the allowance a taxpayer can still only claim the amount they spent. Allowances are paid in advance as part of payroll processing.
Reimbursements
Reimbursements made to employees are exact compensation for actual expenses incurred. The employer may be subject to fringe benefits tax (FBT) depending on the nature of the travel. If the reimbursement is covered by FBT, the amount is deductible to the employer, it is not assessable income to the employee, and the employee cannot also claim a deduction. If it is not subject to FBT, because the expense is deductible, then it is also not assessable or deductible by the employee.
Reimbursements are paid in arrears and may be paid as part of payroll processing or external to payroll as an expense.